Using the Tools
Introducing the Tools
In Brightcove Beacon the wrench icon (labeled 1) represents a set of tools. The options for the tools are Ingestion and Cache (2). This document explores the two options.
Ingestion
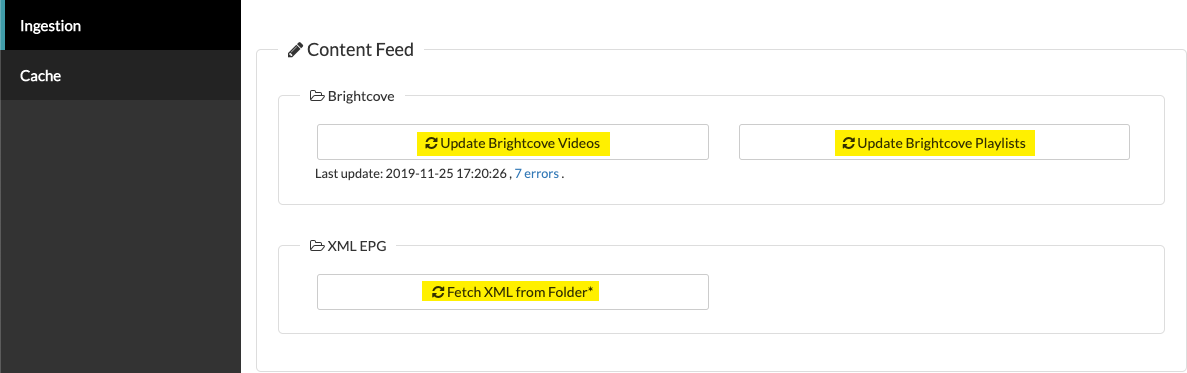
In the Ingestion group you have three tools:
- Update Brightcove Videos: If you have added videos to your Video Cloud catalog, or altered existing videos, this button syncs the newly added or updated videos to Brightcove Beacon.
- Update Brightcove Playlists: If you have added playlists to your Video Cloud catalog, or altered existing playlists, this button syncs the newly added or updated playlists to Brightcove Beacon.
- XML EPG - Fetch XML from Folder: When your EPG (Electronic Program Guide) needs to be updated, this button retrieves the updated XML file. You will be provided an S3 account in which to drop the file.
Caveats for ingestion
Note that not all data that is entered about a particular video in Studio is automatically ingested into Brightcove Beacon. For instance, the following are not ingested into Brightcove Beacon from Video Cloud:
- Availability times: Scheduling times set in the AVAILABILITY section of the video's properties are not ingested into Brightcove Beacon. The dates will be, but not the times.
- Geo Filtering: Geo filtering information set in the AVAILABILITY section of the video's properties are not ingested into Brightcove Beacon.
Also note that not every field mentioned in Brightcove Beacon has an associated custom field. For instance Production Country and Sub-Genre do not have corresponding custom fields associated with them.
Cache
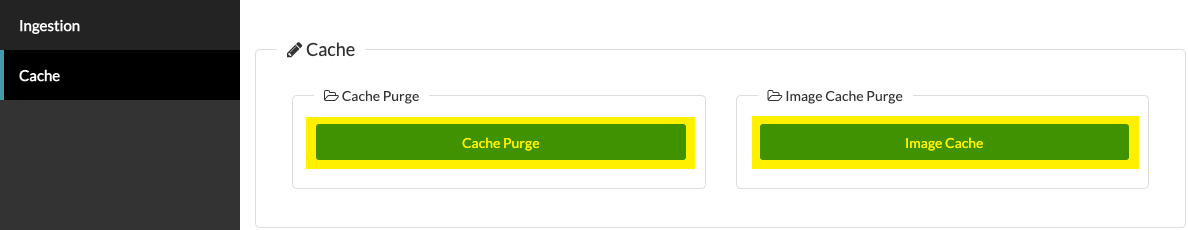
In the Cache group you have two tools:
- Cache Purge: When you make changes in Brightcove Beacon, click this button to roll those changes into the current configuration. This option pulls all changes EXCEPT images into the current configuration.
- Image Cache: If you update any images in Brightcove Beacon, click this button to roll the image changes into the current configuration.
This process should not be done indiscriminately as doing this too frequently in production has an adverse effect on scalability and performance.
